end tidal co2 range in cardiac arrest
Now with continuous end tidal capnography providers have access to so much more information during a cardiac arrest resuscitation as summarized by the recently released 2015 American Heart Association AHA recommendations. Therefore if you have circulationperfusion----end result will be production of CO 2.

Use Capnography For A Patient In Cardiac Arrest Capnoacademy Capnoacademy
In the first minute of ventilation after cardiac arrest the etCO 2 was significantly decreased in the PE group 6509 versus both hemorrhage 16511 and TTX 34224 torr.
. CO2 values are lower in the four hours prior to cardiac arrest patients in comparison to the four hours prior to a hypotensive event. Uses during cardiac arrest. The purpose of this study was to evaluate ETCO as a quantitative marker of cardiac arrest in a human model of ventricular fibrillation VF.
The primary outcome variable was attaining return of spontaneous. It can also help determine the. End Tidal CO 2 5 Continuous PETCO 2 in line between airway and BVM or ventilator circuit.
Gradual fall in ETCO2 suggests compressionist fatigue during CPR - time to change compressionists abrupt increase in ETCO2 suggests ROSC during CPR detectable before pulse check ETCO2 at 20 minutes of CPR is prognostically useful Prognosis 20 mmHg at 20 minutes CPR - higher chance of ROSC. Waveform capnography should be monitored in all intubated patients and displayed on the monitor as above. However in ACLS and in a cardiac arrest Im using end-tidal not necessarily for the pulmonary or respiratory status but to look at the function of the pump the function of the heart.
Because impaired circulation during arrest causes CO2 to. For example a patient compressed to 20 ATA may have an actual end-tidal. CO2 levels are lower overall in cardiac arrest patients in comparison to normal patients.
And then ETCO 2 can be measured. CO2 levels 5 hours prior to hypotension or acute withdrawal of care were not significantly different than cardiac arrest see Table. Thirtyone cardiac arrestVF episodes mean BP 40 mmHg in 8 men and 3 women mean age 42 24 years.
Mean end-tidal carbon dioxide 5 minutes prior to inhospital cardiac arrest was significantly lower than all evaluated time points except 180 minutes p 005. The objective of this study was to evaluate initial end-tidal CO2 EtCO2 as a predictor of survival in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Because the patient is compressed and the analyzer is calibrated at atmospheric pressure the measured end-tidal carbon dioxide values must be corrected for interpretation.
A low end-tidal CO2 may indicate poor perfusion hypovolemia or sepsis. The first aim of the study was to investigate whether arteriolealveolar carbon dioxide difference AaDCO2 which is calculated using blood gas parameters and end-tidal carbon dioxide EtCO2 which is measured by capnography could be used as prognostic markers for patients with cardiac arrest in which ROSC is provided. Remember a normal end-tidal is between 35 and 45.
A sudden increase in ETCO2 is often the first sign of return of spontaneous circulation ROSC even before a carotid pulse can be detected. This was a retrospective study of all adult non-traumatic out-of-hospital cardiac arrests during 2006 and 2007 in Los Angeles California. Thirtyone cardiac arrestVF episodes mean BP 40 mmHg in 8 men and 3 women mean age 42 24 years.
EtCO2 is a measurement of the partial pressure of CO2 in gas expired at the end of exhalation when exhaled gas will most closely resemble the alveolar CO2 concentration. The purpose of this study was to evaluate ETCO as a quantitative marker of cardiac arrest in a human model of ventricular fibrillation VF. The initial values of PetCO2 were significantly higher in the group with asphyxial cardiac arrest 674 422 kilopascals kPa versus 451 247 kPa.
In a state of perfect equilibrium arterial and end-tidal CO 2 levels correlate on a 11 basis. Known as the arterial-to-etco2 gradient this differential results from small amounts of dead-space ventilation ventilation without perfusion and a slight venous admixture. Between June 2006 and June 2009 resuscitation was attempted in 325 patients and in this study we included 51 patients with asphyxial cardiac arrest and 63 patients with VFVT cardiac arrest.
Remember CO 2 is a result of tissue metabolism and circulation. A ETCO 2 ETCO 2 levels do seem to provide limited prognostic information for patients who have experienced cardiac arrest. Although the normal range for CO2 should be between 35-45mmHg CO2 monitoring gives healthcare providers a lot more insight into what is going on with a patients condition.
Goals of this investigation. In multivariate logistic regression modeling for return of spontaneous circulation a greater change in the prearrest end-tidal carbon dioxide maximum to prearrest end-tidal. Massive PE with shock decreases the etCO 2 and increases the dead space fraction to a greater extent than hemorrhagic shock at the same MAP.
I can look at those numbers and adjust my ventilator accordingly to keep them within a normal range. For monoplace chambers exhaled gas can be passed out through the chamber hatch to the end-tidal carbon dioxide analyzer. Sensor links to monitor displays numeric ETCO 2 and waveform.
Respiratory end tidal CO 2 ETCO is a marker of pulmonary blood flow and possibly cardiac arrest. But even in an ideal physiologic state a difference of 2 to 5 mm Hg usually exists. Respiratory end tidal CO 2 ETCO is a marker of pulmonary blood flow and possibly cardiac arrest.
One patient survived to hospital discharge. After 20 minutes of advanced cardiac life support end-tidal carbon dioxide SD averaged 4429 mm Hg in nonsurvivors and 32874 mm Hg in survivors P 0001. What is end-tidal CO2 etCO2.
For many years end tidal CO2 monitoring initially was helpful in differentiating tracheal versus esophageal intubations. Initial ETCO 2 or 20-min ETCO 2 20mmHg appears to be a better predictor of ROSC than the 10mmHg cut off value.

Cardiac Arrest Algorithm Acls Algorithms Com

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project
Cardiac Arrest Cpr Defibrillation Medications Airway Em Cases
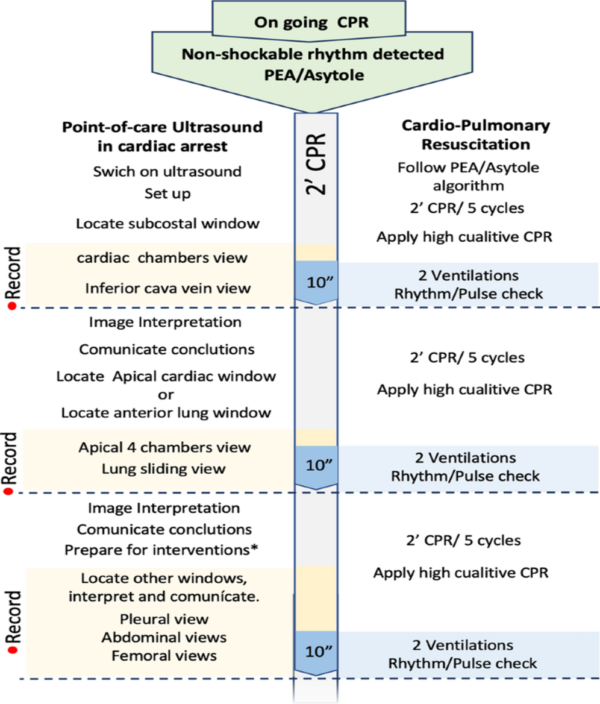
Cardiac Arrest Pocus Communication Ecpr Termination Em Cases

Etco2 Valuable Vital Sign To Assess Perfusion The Airway Jedi

Cureus Algorithm To Improve Resuscitation Outcomes In Patients With Traumatic Out Of Hospital Cardiac Arrest

Clinical Rationale Textbook Hey Guy I Have Been Asked To Talk About Capnography Or Etco2 Monitoring With This Now Being Introduced For Als In Cardiac Arrest Outside Of Cardiac Arrest This
Promed Certifications Algorithms Post Cardiac Arrest Care Acls Algorithm
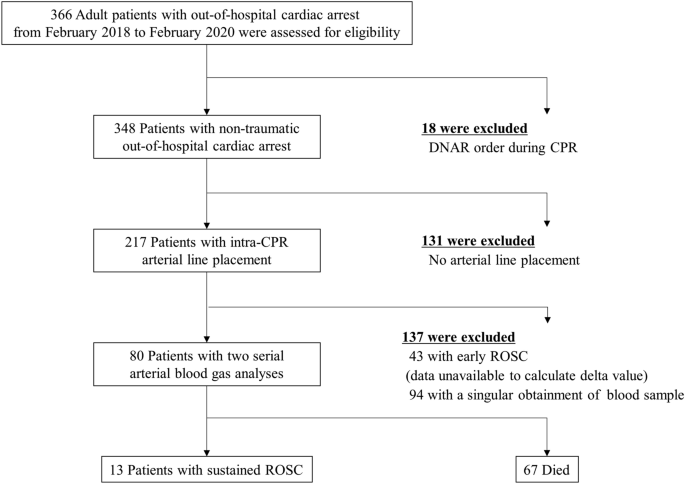
Dynamic Changes In Arterial Blood Gas During Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation In Out Of Hospital Cardiac Arrest Scientific Reports

Quantitative Waveform Capnography Acls Medical Training

Systemic Effect Of Cardiac Arrest And Clinical Implications In The Download Scientific Diagram

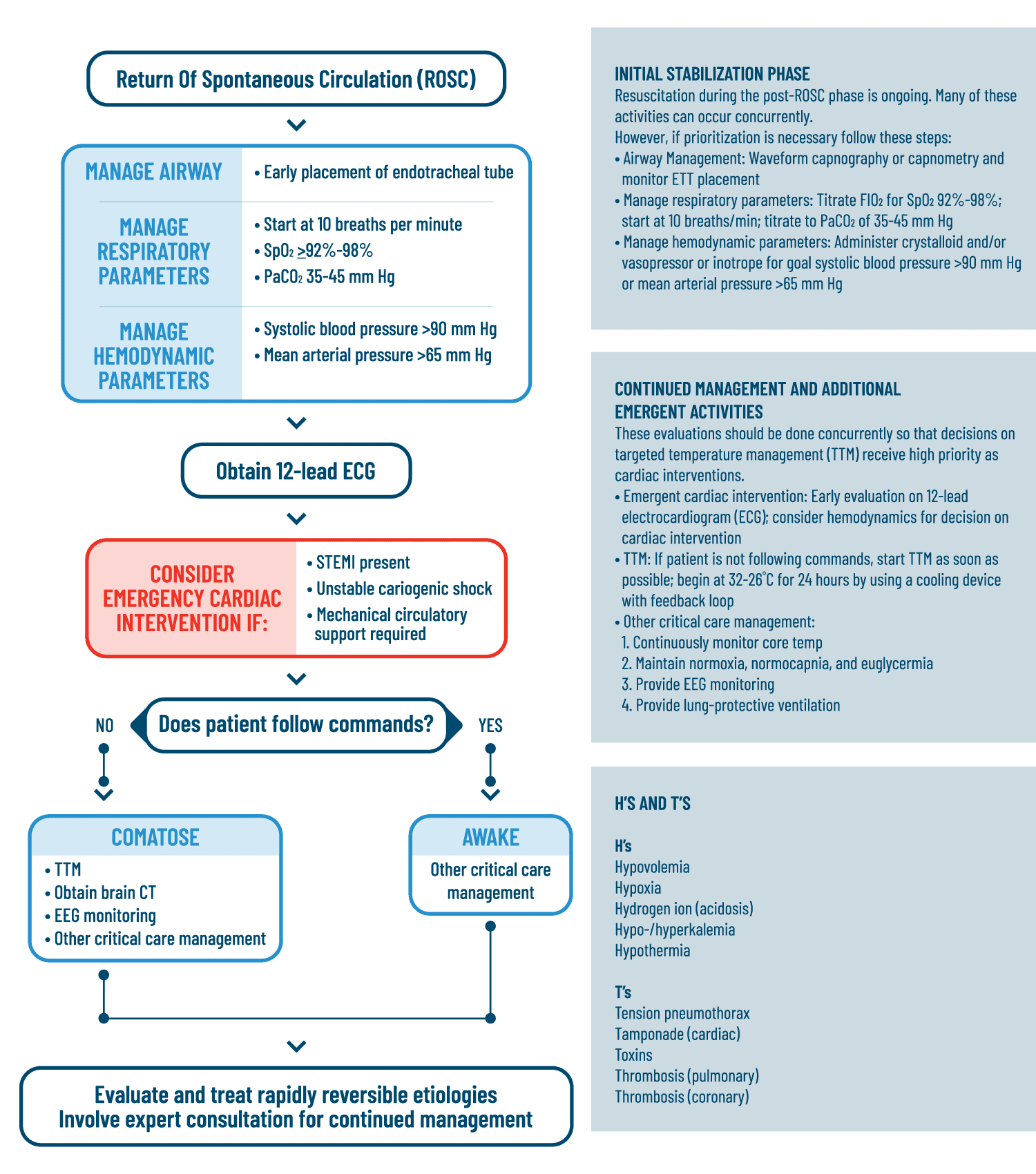
Post Cardiac Arrest Care Acls Algorithms Com

The Use Of End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Etco2 Measurement To Guide Management Of Cardiac Arrest A Systematic Review Resuscitation

Average Etco2 Kpa During Cpr In Patients With Or Without Rosc Download Scientific Diagram

End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Etco2 And Ventricular Fibrillation Amplitude Spectral Area Amsa For Shock Outcome Prediction In Out Of Hospital Cardiac Arrest Are They Two Sides Of The Same Coin Resuscitation

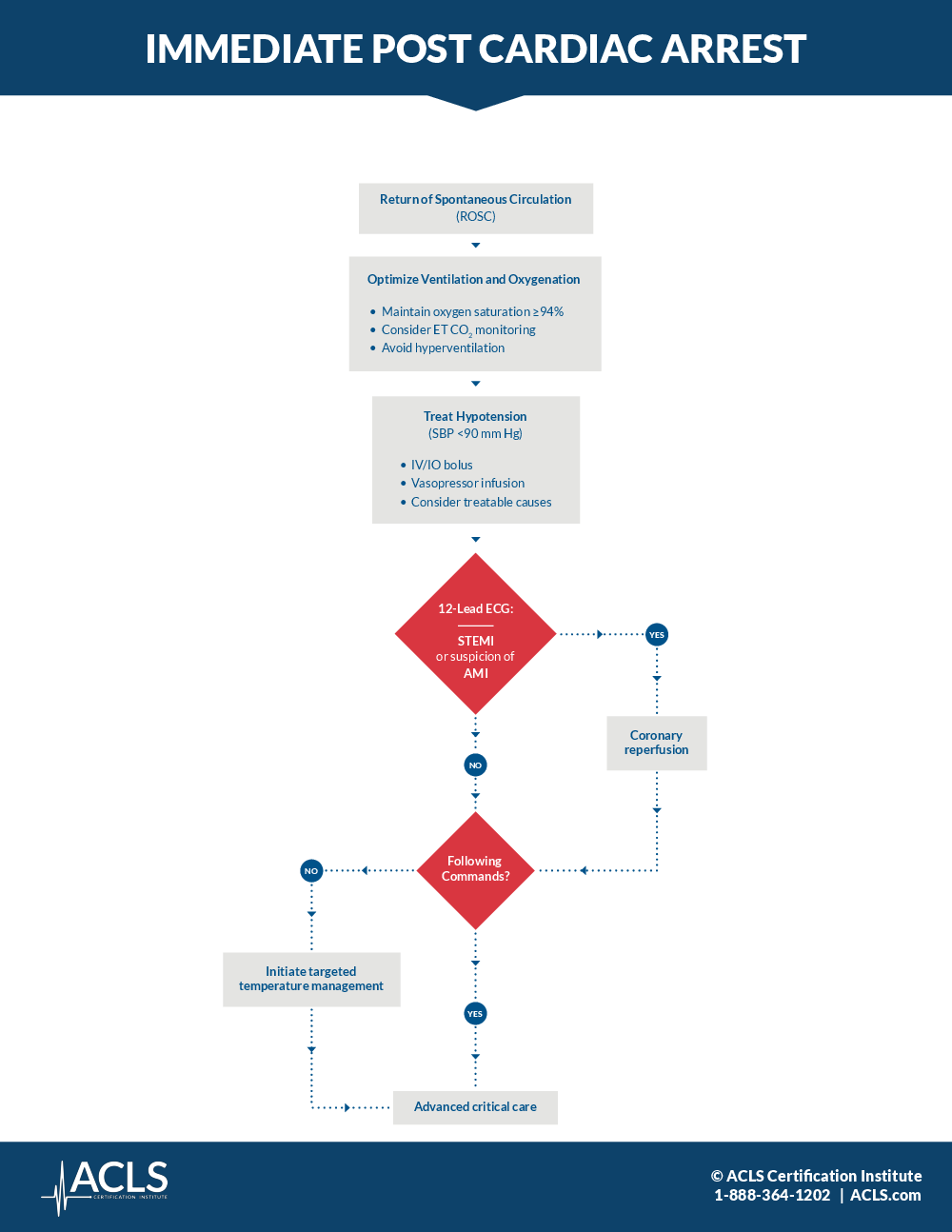
Immediate Post Cardiac Arrest Care Algorithm Acls Com Resources

Early Ecpr For Out Of Hospital Cardiac Arrest Best Practice In 2018 Resuscitation

Abstract 223 End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Levels Predict Cardiac Arrest Circulation
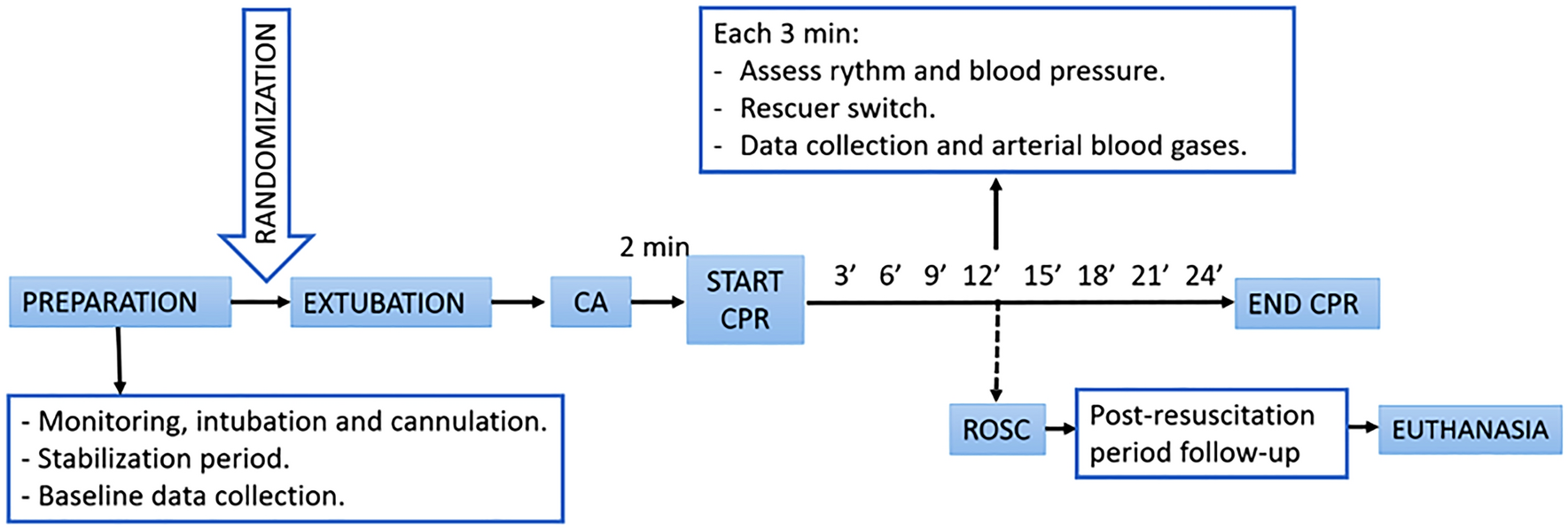
Effects Of Airway Management And Tidal Volume Feedback Ventilation During Pediatric Resuscitation In Piglets With Asphyxial Cardiac Arrest Scientific Reports